Lesson: Overview of the Java 2D API Concepts
Java 教程是为 JDK 8 编写的。本页中描述的示例和实践未利用在后续版本中引入的改进。
坐标
The Java 2D API maintains two coordinate spaces:
- User space – The space in which graphics primitives are specified
- Device space – The coordinate system of an output device such as a screen, window, or a printer
User space is a device-independent logical coordinate system, the coordinate space that your program uses. All geometries passed into Java 2D rendering routines are specified in user-space coordinates.
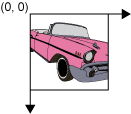
When the default transformation from user space to device space is used, the origin of user space is the upper-left corner of the component’s drawing area. The x coordinate increases to the right, and the y coordinate increases downward, as shown in the following figure. The top-left corner of a window is 0,0. All coordinates are specified using integers, which is usually sufficient. However, some cases require floating point or even double precision which are also supported.
Device space is a device-dependent coordinate system that varies according to the target rendering device. Although the coordinate system for a window or screen might be very different from the coordinate system of a printer, these differences are invisible to Java programs. The necessary conversions between user space and device space are performed automatically during rendering.